Having a 401(K) plan with your employer gives you an edge when it comes to retirement saving and financial planning. The 401(k) contribution limits are higher than IRA contribution limits in any given year which makes them superior. For 2024, the 401(k) contribution limit is $23,000 or $30,500 if you are 50 or older. For 2023, you can contribute up to $22,500 and an extra $7,500 catch-up contribution if you are 50 or older. Any contribution you make to your pre-tax 401(k) is tax deductible. This means that you delay paying tax on the account until retirement when you are taking distributions.
Many employers also match your contributions up to a certain percentage which is free money that boosts your retirement savings. For example, your employer can match your contributions up to 6% of your gross income. Some employers require that you work in the company for a given number of years before you are fully vested.
If you are getting an employer match, your contribution together with the employer match should not exceed $66,000 in 2023 and $69,000 in 2024.
What is a 401(K) plan?
A 401(K) plan is an employer-sponsored retirement savings account that helps qualified employees save for their retirements. Contributions to your 401(k) plan come from your wages through payroll deductions. On top of your contributions, your employer might also match your contributions up to a certain percentage usually between 3% to 6% of your gross income.
Your employer’s contribution is like free money to your account. Some employers especially those that match your contribution at a higher percentage have vesting schedules. That is you must work for the company for a given number of years before you can own 100% of your employer’s contributions. Leaving the company before you are fully vested can result in losing some of the money your employer contributed to the plan.
A 401(K) plan also restricts you from withdrawing your funds before retirement and a penalty may apply if you violate this rule. The IRS requires that you turn 59½ before you can take distributions from your 401(K) without paying a 10% penalty.
Pre-tax 401(K) contribution limits in 2023
Although you are encouraged to contribute as much as possible, there is a limit to how much you can contribute to your 401(K) plan. The max contribution limit to your 401(k) in 2023 is $22,500 with an extra $7,500 catch-up contribution if you are 50 or older. That is if you are at least 50 years old, you can contribute $30,000 to your 401(K) plan in 2023.
Pre-tax 401(K) contribution limits in 2024
The 401(k) contribution limits for 2024 are $23,000. If you are 50 or older, you can make an extra catch-up contribution of $7,500 for a total contribution of $30,500.
Roth 401(k) contribution limits in 2023
The Roth 401(k) plan is like a pre-tax 401(k) but with the Roth plan, your contributions come from after-tax wages through payroll deductions. This allows you to grow your account tax-free and pay no income tax on qualified distributions just like your Roth IRA.
For 2023, the Roth 401(k) contribution limits are $22,500 and if you are 50 or older, you can make an extra catch-up contribution of $7,500.
Roth 401(k) contribution limits in 2024
For 2024, the Roth 401(k) contribution limits are $23,000 and if you are 50 or older, you can contribute an extra catch-up contribution of $7,500 for a max contribution of $30,500. The 401(k) max contribution limits are the same for both the Roth and pre-tax 401(k).
How much should I contribute to my 401(K) plan?
The answer to this question varies from one person to another. This is because we all have different financial situations which dictate the decisions we make. Also, having different age directly affect your contribution limit.
The following are tips to decide how much to contribute to your 401(K)
- Put away the limit allowed by the IRS. If you can afford it, contribute the maximum allowed by the IRS. That is you will contribute $22,500 in 2023 or $23,000 in 2024. Putting away a lot of money reduces your taxable income and helps maximize your tax benefits.
- Contribute up to your employer’s matching percentage. If you have a 401(K), try to contribute at least to your employer match. Since the matching percentage is free money and its dollar value depends on how much you contribute; make your contributions equal to the matching percentage. This way you will not be leaving free money on the table.
- Contribute what you can afford. If you can afford it, consider contributing between 10-20% of your income assuming you do not go over the 401(K) contribution limit. But if you cannot afford this amount, contribute what you can afford given your financial situation since most accounts allow you to contribute as little as 1% of your income.
Related: How much should you contribute to your 401(K) account
Why older people must contribute more to their 401(K)?
People who are older should contribute as much as possible. Getting closer to your retirement means that you will have fewer years to contribute to your plan. In addition, long-term investments are the best way to build wealth due to compound interest. Getting closer to your retirement, however, reduces your chances of taking full advantage of compound interest. To leverage this situation, older people must contribute a lot of money to their retirement accounts.
Younger people, on the other hand, have a lot of years ahead of them. Having many years, however, does not mean you should put away a tiny amount and chill. You still need to take your retirement planning seriously and make adequate contributions to your 401(k). The earlier you contribute and the more you contribute, the better.
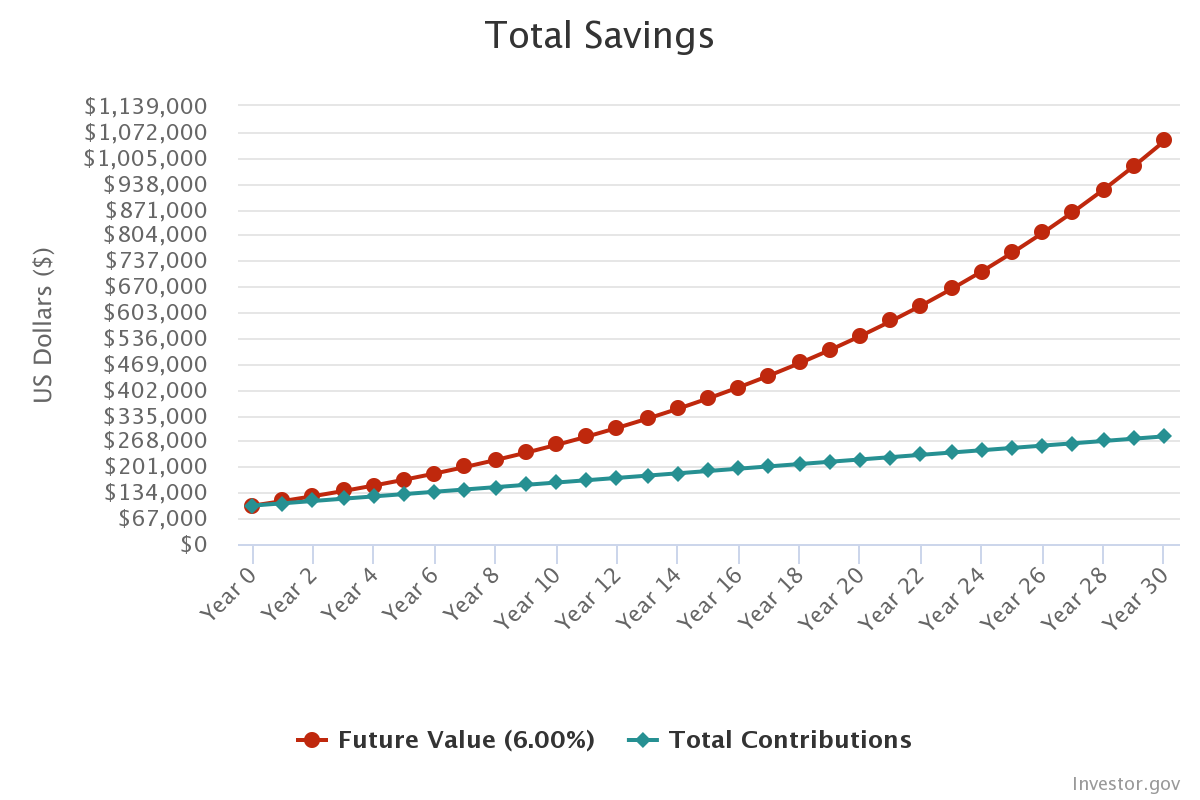
The graph above shows the power of compound interest. As you get started, your contribution will not make that much of a difference. However, the interest you earn on your investment gets reinvested which creates exponential growth over time.
Starting early and contributing as much as possible helps you reach financial independence much faster. So, if you are younger, start contributing to your 401(k) as soon as you get your first job. You can also open other retirement plans such as IRAs.
Related: Compound Interest Definition
What are the benefits of a 401(K) plan?
Your pre-tax 401(K) plan is a tax-advantaged retirement account where your contributions are tax-deductible. This automatically reduces your taxable income and allows you to grow your savings without paying taxes until you are taking distributions.
On top of these tax benefits, your employer can give you free money through contribution matching.
Here are the pros and cons of 401(k) plans and what you should expect from making regular contributions.
Pros of 401(K):
- 401(k) reduces your taxable income
- It helps you build wealth and pay taxes later
- You can get free money through employer matching
- Your 401(k) plan can help you reach your retirement goals much faster
- It comes with higher contribution limits compared to other retirement accounts
What are the drawbacks of the 401(K) plan?
Having a 401(K) plan does not mean you are off the hook. The money in the account will be invested and your account will be managed by the plan provider. The people who conduct all these activities for you will be paid. That is why there are fees and charges you pay on your 401(K) account.
Since your 401(K) account is tax-advantaged, you will pay a penalty if you withdraw money from the account before retirement. The government agreed to not charge you tax, and in return, you promised to not withdraw the money until you are in retirement. That is why premature withdrawals automatically lead to a 10% penalty.
Here are the cons of 401(k) plans.
Cons of 401(K):
- It comes with a 10% early withdrawal penalty
- There is a limit to how much you can contribute
- You will pay income tax on your distributions during retirement
- The 401(K) plan comes with high fees
- 401(k) comes with required minimum distributions(RMDs)







