What is asset coverage ratio?
The asset coverage ratio is a financial ratio that measures the ability of a company to repay its debts by liquidating its tangible assets. Liquidation refers to the sale of all company’s tangible assets to cover its financial obligations. That is the company comes to an end as its assets are converted into cash to pay all entities and investors that hold liens on its assets.
Before investors lend money to a business they will need to assess its creditworthiness. The following is one of the most important questions investors will need answers for. Does the company have enough tangible assets to pay us back if it is to be liquidated?
Fewer tangible assets and more liabilities reduce the asset coverage ratio. Companies with a small ratio are risky, and therefore, investors do not favor them. This makes it very difficult for a company with fewer tangible assets to raise money from investors.
How to calculate the asset coverage ratio?
To calculate the asset coverage ratio, you will use the following formula, according to Ready Ratios. The formula relies on assets, liabilities, and debts.

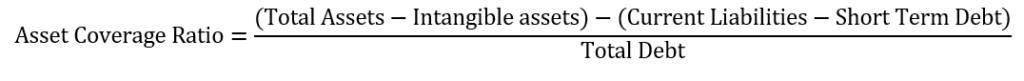
Example
Let’s assume that ABC company reported the following information on its balance sheets.
- Current Liabilities = $50,000
- Intangible Assets = $180,000
- Total Assets = $450,000
- Short-term Debt = $15,000
- Total Debt = $135,000
What is the assert coverage ratio?
To calculate this ratio, will just put these numbers into the above formula. If you are using an actual financial report, you can find all this information on the balance sheet.
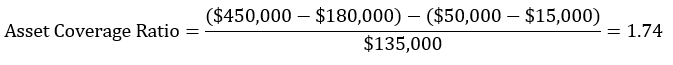
From these calculations, ABC company has an asset coverage ratio of 1.74. In other words, if the company is liquidated, its tangible assets can cover its debt 1.74 times.
Why does the asset coverage ratio matter?
A higher asset coverage ratio means that a company has enough tangible assets that can cover its debt during insolvency. On the contrary, a lower ratio indicates that the company does not have enough assets to cover its debt.
The asset coverage ratio helps investors to understand how much risks they will be exposed to by investing in the company. A low ratio indicates that a company is risky since it would be difficult for investors to recover their funds.
Moneylenders such as banks, credit unions, and lending institutions use asset coverage ratios to examine a companies’ creditworthiness.
Lenders do not like companies with fewer assets. As a result, companies that are not well established without enough assets, find it difficult to raise money. Why would a lender give more money to a company if it lacks the means to pay it off?
Furthermore, this ratio comes in handy when comparing two or more companies in the same sector. For example, if you want to invest money in a particular sector, it would make sense to put your money in a company that is more promising than its competitors.
In other words, you would put your money in a company that has enough assets to cover your funds when it comes to liquidation.