What is return on assets?
A return on assets also known as ROA is a performance ratio that shows the profitability of a company based on its total assets, according to Bankrate. Investors use this ratio to understand how the management team uses the company’s assets to generate income. The ratio is usually expressed as a percentage. The higher the ratio the more returns a company generates from its assets.
How to calculate the return on assets or ROA?
The return on assets is calculated by dividing the company’s net income(earnings) with its total assets at a given time. For example, if you want to calculate a yearly return on assets, you would divide the net income with the total assets at the end of the year.
What is the formula of ROA?
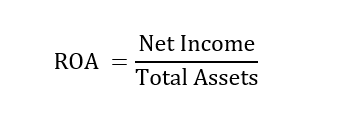
Where,
ROA = Return on Assets
Net Income = Net profit reported on the income statement
Total assets = Assets reported on the balance sheet
Example of return on assets
Let’s assume that Sarah invested $100,000 to buy all assets used for her clothing store. Let’s also assume that she made a net profit of $10,000 after some time. Our job at this time is to calculate her return on assets.
Answer:
Total assets = $100,000
Net Income = $10,000
By plugging these numbers in the ROA formula depicted above, we will get the following results.
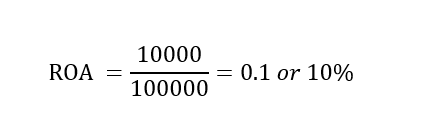
From our example, we can see that Sarah’s clothing store is profitable. That is for every $1 invested in assets, Sarah makes $0.1 in income.
What if there is another store in the same neighborhood and you want to compare their performances?
Well, you can calculate the ROA of the second store and compare it with Sarah’s ROA.
Let’s assume that Mr.V has a store in the neighborhood and he has invested $50,000 in total assets with a net profit of $1,000. By using the same formula, Mr.V’s clothing store will yield a ROA of 0.2 or 2%.
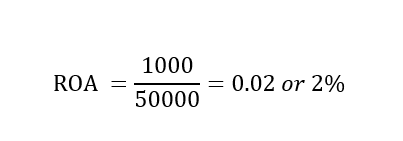
By comparing both businesses, you can see that Sarah’s clothing store is doing much better than V’s store. Although these two numbers will not be the only factors you will use to make your investment decisions, they will give you a strong start in understanding how well these two businesses make money from their invested capital.
Why is the return on assets important ?
When it comes to estimating the performance of a company, profitability and growth are the most important factors that grab investors’ attention. For this reason, the ROA is one of the many factors that will be evaluated.
The ROA is an important ratio that investors use when estimating how well a company converts invested money into income. A higher ROA means that a company is making a lot of profit from fewer assets. Hence, good use of its invested money (assets).
On the other hand, a lower ROA signifies that the company is losing money on its invested capital. This raises a red flag as investors wonder if the company will someday be able to generate enough returns on its assets and increase its profitability.
This ratio can also help investors to compare multiple companies that are in the same sector. For example, if a retail store has a better return on assets, it will indicate that the company is more profitable and has a better management team. As a result, this company will be a better investment option.
Investors can also compare a company’s historical ROA ratios to understand how well the company performed over the years. If the ROA trend is up, it will indicate that the company is getting better and paving a route to more growth and profitability.
However, if the ROA’s trend is down, it will indicate that the company is losing money on its assets. Unless something is changed fundamentally, the company could continue to lose money. Hence, turning into a bad investment.