What is inventory turnover ratio?
The inventory turnover ratio is a financial metric that calculates how many times a business sold and replaced its inventory in a given time, according to Tradegecko. Turning inventory faster helps businesses to generate sales.
More sales turn into earnings that help companies to pay off debts, fund product development and growth, cover expenses, and keep the business afloat.
How to calculate an inventory turnover ratio?
To calculate the inventory turnover ratio you will need the average inventory in a given period and the cost of goods sold (COGS).
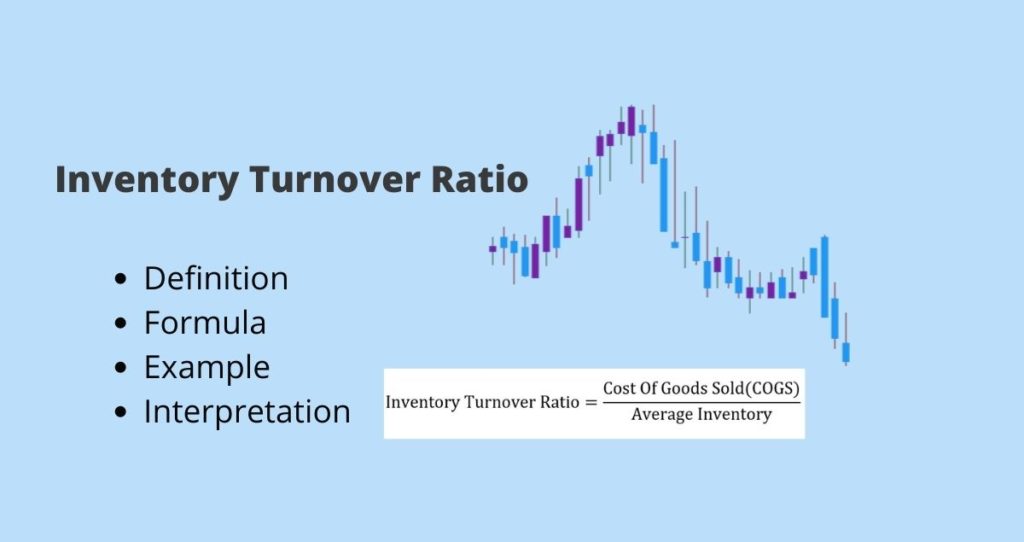
In order words, the inventory turnover is calculated by diving the cost of goods sold by the average inventory in a given time, according to Vend. The following is a formula of the ratio.
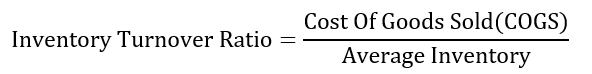
Where,
COGS = Cost Of Goods Sold
Average inventory = The average inventory in a give period = (Beginning Inventory+ Ending Inventory)/2.
Example of inventory turnover ratio
Let’s assume that a company XYZ reported $200,000 and $50,000 of beginning and ending inventories consecutively on its balance sheet for last year. At the same time, the company reported a $600,000 in cost of goods sold.
What is the inventory turnover ratio for this company?
To answer this question, we will use the following steps.
Step 1: List of what we have
- Beginning inventory= $200,000
- Ending Inventory= $50,000
- Cost of goods sold = $600,000
Step 2: Calculate the average inventory for last year
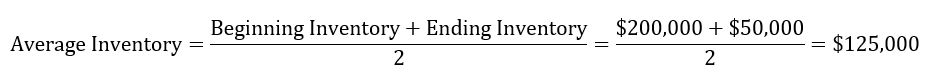
>>Related: Average: What Is The Meaning Of Average?
Step 3: Calculate the ratio
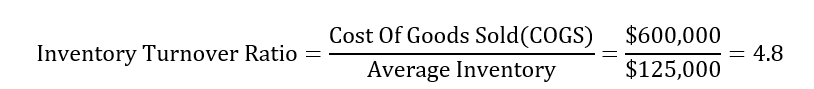
From our calculations, we can conclude that the company XYZ had an inventory turnover ratio of 4.8. In other words, the company sold and replaced its inventory 4.8 times last year.
How to interpret inventory turnover ratio?
A low ratio shows investors that the company’s products stay in its storage for a very long time. In order words, it takes many days to sell its products. Keeping inventory for a long time result in a loss of a lot of money. For example, the company will pay extra money for storage-related expenses and products can end up expiring when they are stored longer.
All these issues lead to a reduction in sales and loss of capital. Without proper adjustments to the business and its management style, the company could fail to pay off its debt or continue its operations.
On the other hand, a high inventory turnover rate shows that the company sells and replaces its inventory in a short time. Inventors interpret a high ratio in two ways. (1) the company is really good at managing its inventory and selling its products and (2) the company does not have enough products to sell.
Option (1) is what every investor expects from companies. The ability to sell inventory in a short time possible increases the companies sales. This in turn increases the earnings and investors’ return on investments.
A high ratio also reflects the quality of the company’s management team.
What is a good inventory turnover ratio?
The turnover ratio will vary from one company to another and from one sector to another. For example, an apparel company can turn its inventory faster than a computer company.
However, good inventory turnover ratio should be between 5 to 10, according to SKUBANA. The higher the better.