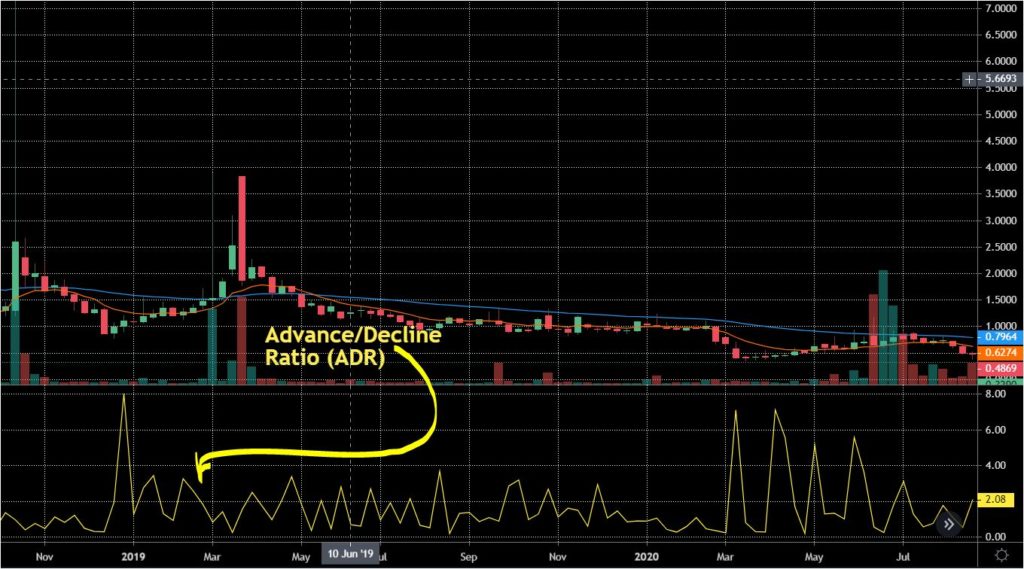
What is ADR?
The advance-decline ratio is a technical analysis breadth indicator. This indicator compares stocks that closed lower than their previous day’s closing price against the ones that closed higher.
In order words, the ADR is the ratio of the advancing shares with the declining shares.
The advancing shares or stocks are those that are increasing in value during a particular trading day.
On the other hand, the declining shares or stocks are those that are losing or declining in value during a particular trading day.
The formula of advance declining ratio (ADR)

This ratio is related to the advancing declining line(ADL). The only difference is that you perform a division instead of a subtraction. Investors use the ADL to assess the performance of the market and to know how many stocks are contributing to the advancement or declining of the market.
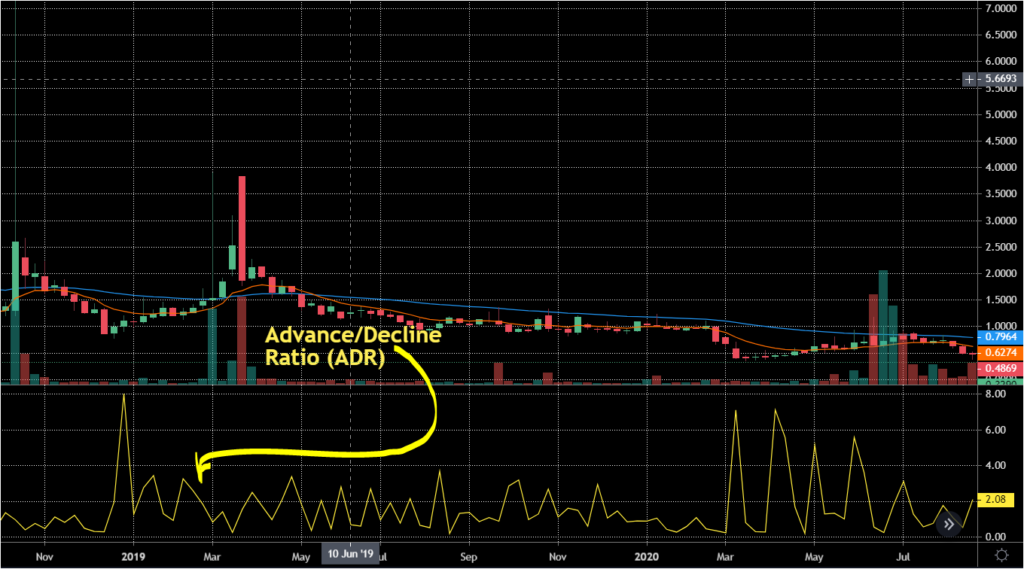
The data from the ADRs can sometimes be hard to interpret due to the high volatility of some stocks. For this reason, the moving average of ADRs can be used to smooth the data(eliminate spikes) for an easy interpretation.
Why is the advance decline ratio (ADR) important?
The ADR ratio is very important as it helps investors to know the market sentiments and trends. For example, if the ratio is increasing over time, investors will have optimistic sentiments about the market. This will could be a strong signal for a bullish market.
At the same time, if the ADR ratio is declining over time, it will mean that more stocks are closing lower than they opened. This will be an indication of a possible bearish market.