What is return on equity?
The return on equity is a financial performance ratio that measures the profitability of a company in relation to its shareholder’s equity, according to CFI. This ratio is measured from the corporation’s net income and its shareholder’s equity. The return on equity is expressed as a percentage.
The income is listed on the income statement whereas the shareholder’s equity is found in the balance sheet.
How to calculate the return on equity (ROE)?
To calculate the return on equity, the net income is divided by the shareholder’s equity. The result is then multiplied by 100.
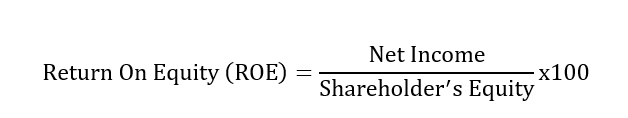
A higher ROE means that the company’s management team makes good investment decisions that return the highest income for its shareholders.
On the other hand, a low ROE means that the company does not invest the shareholders’ money wisely which ends in a loss or poor returns. Investors do not like companies with poor returns on equity.
Why does the return on equity matters ?
The return on equity ratio has a lot of advantages as it helps investors to understand how well a company uses its shareholders’ equity to generate more income.
An ROE can also be used to compare a company’s performance with others in the same sector. For example, if a company has a higher ROE compared to the average ROE in the sector it will indicate that the company is doing much better in that sector. This could be a great investment opportunity for investors.
Furthermore, the historic ROE of a corporation can help investors to know how the company has been performing over time. If the ROE has been going down over time, it will indicate that the company has been making bad investment decisions that resulted in a decline in shareholder’s returns.
The opposite is also true. That is if the ROE increased over time, the company’s returns for every dollar invested have been growing. Only good and well-managed companies can achieve these returns.