What is a loan-to-value ratio?
A loan-to-value ratio is a ratio between the borrowed money to the appraised value of the property, according to Redfin. This value is always expressed in percentage. The appraised value is the estimation of the value of the house that is conducted by an appraiser.
Formula and example of LTV Ratio.
To calculate your LTV ratio, you will divide the money you borrowed by the appraised value, and then multiply the answer by 100.

Where,
LTV ratio = Loan-to-value ratio
Borrowed money = The total amount of money you borrowed from the lender
Appraised value = The value of a home assessed by a professional appraiser during the loan origination process.
Let’s assume that you are buying a house appraised for $200,000 and you are putting down $50,000. In this case, your total mortgage will be $150,000. To calculate the LTV ratio you will divide the money you are borrowing by its appraised value and then multiply by 100.
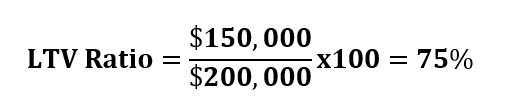
What if you have multiple loans on the house?
If there are multiple loans on a house, you would need to calculate the combined loan-to-value ratio or CLTV in short.
From our example, let’s assume that you had a $150,000 outstanding balance and wanted $20,000 more to build a garage. In this case, your total borrowed money will be ($150,000 + $20,000) which is equal to $170,000.
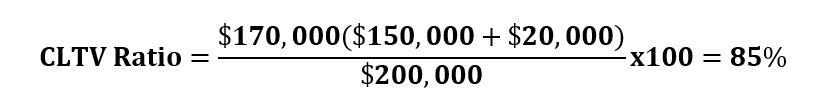
You can see that as the money you borrow increases, the ratio increases as well. I higher LTV may not look good from the lenders’ perspective. A higher LTV implies that you are buying the house almost entirely on a loan.
What is a good loan-to-value ratio?
As noted by Experian, an LTV ratio of 80% or less is considered good for conventional mortgages. However, other forms of loans can accept a much higher LTV ratio. For example, an LTV of 96.5% would work FHA loan since you can get a mortgage for as little as a 3.5% down payment.
How to lower a loan-to-value ratio?
Since your LTV ratio will depend on two variables (down payment and the total appraised value of the house), you must adjust these variables to reduce your LTV ratio. In other words, your LTV ratio will depend on the value of the house and your down payment.
The value of the house you are buying could increase the ratio. Buying an affordable house will put less stress on your budget, and as a result, you will put more money toward your house. For this reason, if you want to reduce the LTV ratio, make sure you buy a house that you can afford.
Your down payment will directly impact the LTV ratio. This is because your mortgage value will be the difference between your downpayment and how much the house is costing you. By increasing your down payment, you will cover most of the cost of the house. As a result, your mortgage will be much smaller.
More learning resources
- What Is An Appraisal?
- Appraiser: What Is An Appraiser?
- Loan Estimate: What Is The Loan Estimate?
- Loan Commitment Letter: Basics And Definition
- Capitalization Rate: What Is Capitalization Rate?
- Debt To Income Ratio (DTI): What Is DTI?
- Advance-Decline Ratio (ADR): What Is The ADR?
- Current Ratio: What Is The Current Ratio?
- Debt To Equity Ratio Or Debt-Equity(D/E) Ratio
- Foreclosed Home: What Is A Foreclosed Home?