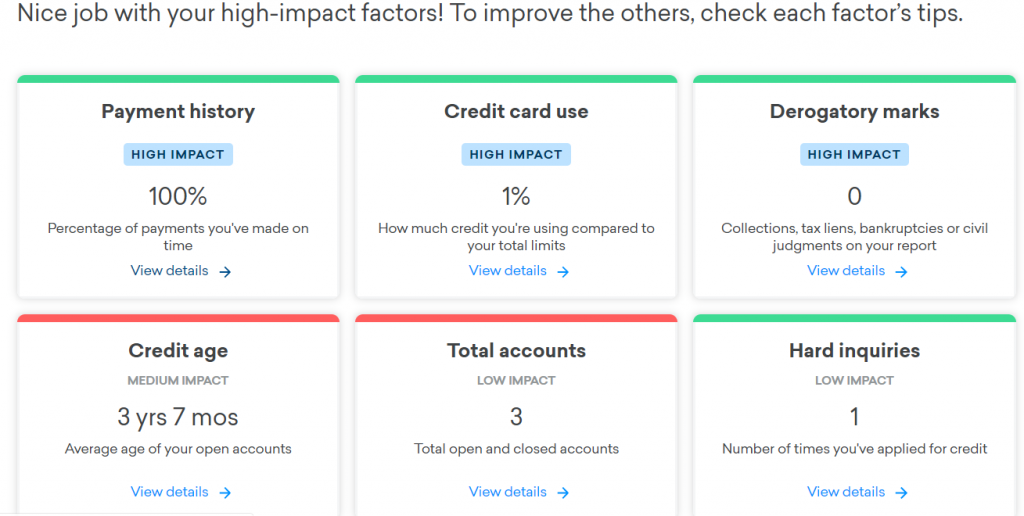
Having a solid credit history and a good credit score allows you to qualify for loans, credit cards, and other services with lower interest rates and better terms. Many factors affect your credit score and knowing the impact of each factor on your credit score is essential especially if you want to build credit. These factors include payment history, credit utilization, age of your credit, credit mix, hard inquiry, and derogatory marks.
Each of these factors contributes a small percentage to your credit score calculation. The biggest factors on your credit score, however, are your payment history(35%), your credit utilization(30%), and the age of your credit(15%). These three factors account for 80% of your FICO score. For the VantageScore, your payment history accounts for 40% of your score while credit utilization accounts for 20% of your score. The age of your credit is usually combined with the credit mix for 21% of credit score calculation.
Here is everything you need to know about all factors that affect your credit score and how each factor contributes to its calculation.
What is a credit card?
Before you learn about factors that affect your credit score, let’s cover the basics of credit cards as they and similar types of credit accounts have a major impact on your credit score. A credit card is a payment card you get from a bank, credit card issuers, and lending institutions. With a credit card, you buy goods and services on credit or withdraw cash. In return, the cardholder pays back the money spent within a billing cycle plus interest accrued on the account.
Each credit card comes with a credit limit which is the maximum amount you can spend on the card. The total amount you owe on a credit card compared to your credit limit is your credit utilization. Keeping your credit utilization low is essential for maintaining good credit and improving your credit score.
Credit cards come with very high Annual Percentage Rates (APRs) compared to other types of loans. The credit card APR usually ranges between 18% to 29.53% with 24.66% being the average credit card APR for new accounts, according to LendingTree. Most credit card companies allow you to make a minimum payment and carry the remaining balance to the following payment period. While this option can be tempting, carrying a balance on your credit card results in a high interest that compounds daily which can easily lead to carrying too much debt.
Related articles:
- Should you carry a balance on your credit cards?
- What happens when you carry a credit card balance?
- What is the best credit utilization ratio?
What is a credit score?
A credit score is a numerical number that ranges between 300 to 850 with 300 being the lowest score you can have and 800 being the highest score you can get. Lenders use your credit score to determine your creditworthiness. The higher your credit score, the more money you can qualify for and the lower the interest rate you pay. A high credit score also qualifies you for other services such as discounted products, deposit waivers on leases, etc.
Typically, having a credit score in the 700s qualifies you for many loans and lower interest rates. To get approved for loans, you should have at least a 640 credit score. Having an 800+ credit score makes you a prime borrower which means you can qualify for any loan at the lowest interest rate assuming that you meet other loan requirements such as a low DTI ratio and income requirements.
There are two major types of credit score which are the FICO score and the VantageScore. Each type of credit score has more variations of credit scores calculated based on different industry requirements. Credit reporting agencies calculate your credit score using information from your credit reports.
Here are 6 factors that affect your credit score.
Related posts:
1. Payment history: High impact on credit score
The biggest factor that affects your credit score is your payment history. The payment history alone accounts for 35% of your FICO score calculation and 40% of your VantageScore. The reason payment history matters the most when calculating credit scores is that paying your bills on time makes you a trustworthy borrower and lenders love that.
People with excellent credit scores (800 scores and higher) do not have negative items on their credit reports. Negative items include but are not limited to late payments, charge-offs, collections, bankruptcies, foreclosure, etc. Here is a complete of all negative items on credit reports. By paying your bills on time, you avoid all these negative items on your credit reports.
Once reported on your credit report, one late payment can lower your credit score by as much as 180 points. Typically, people with high credit scores tend to lose more points than those with low credit scores from a late payment. Most lenders report late payments to credit reporting agencies 30 days after the due date. Other lenders, however, report late payments after 60 days of delinquency.
2. Credit utilization: high impact on credit score
The second highest factor that affects your credit score is your credit utilization. Credit utilization simply refers to how much you owe on a revolving credit account compared to the available credit limit. Revolving accounts include credit card accounts, Home Equity Line of Credit (HELOC), and personal and business lines of credit.
How much does credit utilization affect your credit score? Credit utilization accounts for 30% of your FICO score and 20% of your VantageScore. A high credit utilization indicates that you are relying on debt to finance your expenses which makes you a risky borrower.
The credit utilization is usually calculated as a percentage. For example, if you have a total credit limit of $5,000 and you have spent $3,000, your credit limit will be 60%.
Having a high credit utilization prevents you from qualifying for loans or getting a new credit card account. Most lenders suggest a credit utilization of 30% or under. But, if you need to have a good credit score, pay all your credit account balances in full at the end of each month. This will prevent you from carrying a balance on your credit accounts which will save you money in interest charges and boost your credit score.
If you cannot pay your balances in full, at least keep your credit utilization under 7% for maximum credit score benefits. Even if you have the option to pay the minimum payment, do not fall for this trap. Always pay as much as you can.
Related posts:
- What happens when you carry a credit card balance?
- Should you carry a balance on your credit cards?
- What is the best credit utilization ratio?
3. Credit age: Medium impact on your credit score
The third factor that affects your credit score is the credit age. This factor is sometimes called the age of your credit on some credit reports. The credit age simply refers to how long you have been a credit user. For example, if you opened your first credit card account 5 years ago, the age of your credit will be 5 years. The longer you use credit, the higher your credit score gets and the more established your credit history becomes. A solid credit history allows you to easily qualify for loans at competitive interest and terms.
Using credit for many years helps you build credit history which is essential when you are applying for loans. A good credit age is usually about 10 years. But, this does not mean you cannot have an excellent credit score in a short period. For example, I was able to get an 825 FICO score in less than 5 years.
How much does the age of your credit affect your credit score?
Credit age accounts for 15% of your FICO score and 21% of your FICO score together with your credit mix. While you cannot increase your credit age by force, getting your first credit account as soon as possible is a great way to start working on your credit history.
People with thin credit files usually find it difficult to qualify for credit due to a lack of credit history. A thin credit refers to having little to no credit activities on your credit reports.
How do you calculate the age of your credit?
Credit age is usually the average age of all open accounts you have. To calculate the age of your credit, simply add the credit age of each account you have and then divide the sum by the total number of those accounts.
For Example, if your first credit card was opened 5 years ago, the second credit card opened 3 years ago, and your 3rd card 2 years ago; your credit age will be 3.3 years (average of 5,3, and 2). If you apply for another card now, your credit age would go down since your fourth card would have 0 years on it. So, your new average would be 2.5 years this age might lower your credit score.
4. Derogatory marks: High impact on your credit score
Derogatory marks are some of the biggest factors that affect your credit score and are also known as negative items. You get negative items on your credit reports usually when you fail to pay your bills on time or default on your loans. As I stated in your payment history section, paying all your bills on time is essential to safeguard your credit score.
If you miss a payment or are unable to pay your loans at all, other negative items end up showing up on your credit reports depending on how your loan issue has been resolved. For example, if you default on a mortgage, you might have a foreclosure on your credit report. If you declare bankruptcy due to financial hardships, a bankruptcy will appear on your credit report.
Once reported on your credit report, a derogatory mark/negative item will hurt your credit score and lower your chances of qualifying for credit cards and loans. The number of points you lose usually depends on your credit score and the type of negative item submitted to credit bureaus. For example, you can lose as many as 180 points from late payments and you can lose between 130 to 200 points from bankruptcy depending on your credit score.
Additionally, negative items can stay on your credit report for 7 to 10 years. The bankruptcy is the one that stays on your report for 10 years while every other item stays on your report for 7 years or under.
You might also like:
- 13 common negative items on a credit report
- How does a foreclosure affect your credit?
- How do late payments affect your credit score?
5. Credit mix: Low impact on credit score
Another factor that affects your credit score is your credit mix. The credit mix refers to the different types of credit accounts you have on your credit reports. Lenders prefer consumers who can handle different types of credit accounts such as credit cards, mortgages, loans, etc. Your credit mix accounts for 10% of your FICO score.
A good credit mix should have a combination of revolving credit accounts such as credit cards, HELOCs, and personal or business lines of credit and installment loans credit such as car loans, student loans, and mortgages. While having these loans can improve your credit mix and boost your credit score, you don’t need all these loans to improve your credit score or get an excellent credit score.
As long as you respect the terms of your loan and respect other factors that affect your credit score, you can easily get a high credit score. For example, I was able to raise my credit score to 825 with three credit cards. Learn how to get an 800+ credit score with this simple guide.
Taking on too many loans increases your debt-to-income (DTI) ratio which keeps you in debt for a while. A high DTI ratio also increases your chances of missing a payment and lowers your ability to qualify for loans and credit cards. For this reason, you should take out loans only when you need them instead of borrowing simply because you want to have a good credit mix.
6. Hard inquiries: Low impact on your credit score
The last factor that affects your credit score which is also very common is a hard inquiry. Hard inquiries account for 10% of your credit score.
So, what are hard inquiries and how do they work?
A hard inquiry appears on your credit report when you apply for credit. For example, if you reach out to your bank for a mortgage, you will see an inquiry on your credit report, and your score will drop by 5 to 6 points.
Every time you apply for credit, the lender requests to view your credit profile to access your creditworthiness. The fact that you are trying to borrow money translates to a reduction in creditworthiness which results in a hard inquiry on your credit report. To maintain good credit, you should have no more than one hard inquiry on your credit report in any consecutive 12 months.
Each hard inquiry stays on your credit report for 24 months but it only affects your credit score for 12 months. After 2 years, the hard inquiry automatically falls off your credit reports. If you have a hard inquiry that is older than 24 months on your credit reports, dispute it to major credit bureaus. Here is a guide on how to dispute errors, negative items, and fraudulent activities on your credit report.
Read more: How long do hard inquiries stay on a credit report?
Final words
Building credit and improving your credit score can be easy or hard depending on how you do it. The easiest way to improve your credit score is to understand factors that affect your credit score and focus on them one by one. For example, paying your bills on time helps you maintain a good credit score as your payment history affects 35% of your FICO score and 40% of your VantageScore.
Other factors that affect your credit score include credit utilization, hard inquiries, the age of your credit, credit mix, and derogatory marks. By paying your bills on time, avoiding excess borrowing, and spending wisely, you can easily build a solid credit history and get a good credit score. A good credit score allows you to qualify for loans with better terms.