Credit scores come in many forms, types, and ranges. Lenders use your credit score to evaluate your creditworthiness. A good credit score can help you qualify for many financial products, including mortgages, loans, credit cards, etc, as the risk of lending you money is low. With a bad credit score, however, you will not have access to most of these financial products as lower credit scores indicate potential risks of loan defaults. This article will walk you through what is considered a bad credit score and how you can improve your credit score.
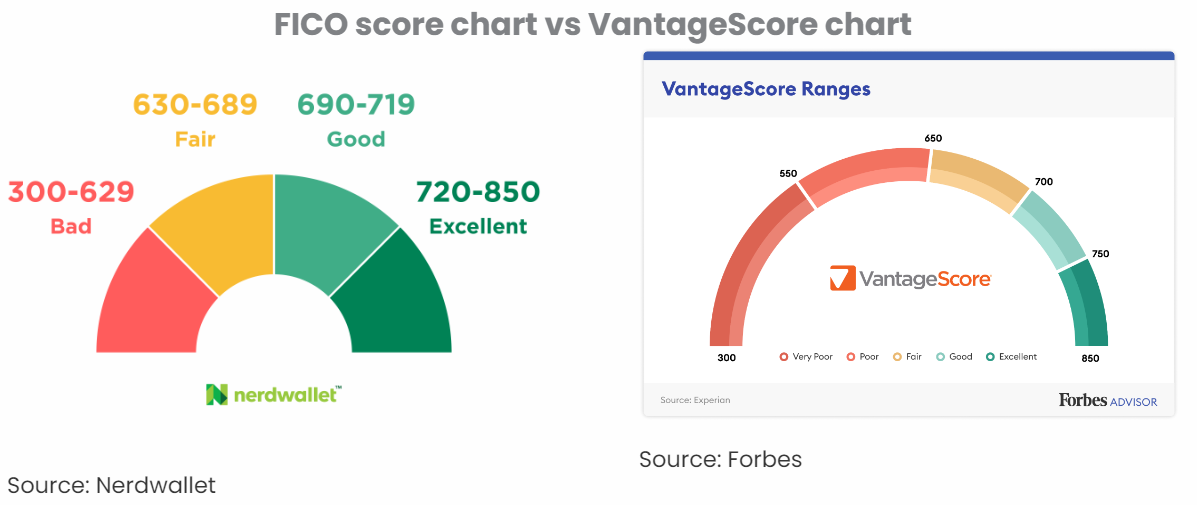
Since there are different scoring models, the ranges of credit scores will differ from one model to another. A bad FICO score is any score between 300 and 579, whereas a VantageScore is considered bad when it is between 300 and 600.
What is a credit score?
A credit score is a three-digit number that ranges from 300 to 850. This range is divided into smaller ranges that make up your credit score chart. The lowest score you can have is 300, and the highest score you can have is 850. Your score exceeds this range, so you qualify for many financial products at lower rates, including loans and credit cards.
Since there are different credit scoring models, each person will have different credit scores. The two major credit scoring models are the FICO Score and VantageScore models.
The Fair Isaac Corporation(FICO) calculates the FICO score. Your VantageScore, on the other hand, is calculated by the three major credit reporting agencies(Experian, TransUnion, and Equifax).
What is a bad credit score?
What is considered a bad credit score depends on where you stand on the score chart and the model used to calculate your score. Different lenders also judge credit scores differently. For example, a credit score considered bad for insurance companies could be okay for auto loan providers.
Let’s compare credit score charts from the two most well-known credit scores(FICO score and VantageScore) to help explain what is considered a bad credit score.
FICO scores and VantageScores models apply different weights to the information they use when calculating your credit scores. For example, your payment history accounts for 35% of your FICO score calculation and 40% of your VantageScore calculations.
These variations in scoring models result in different credit scores from credit reporting companies.
So, what is a bad FICO score?
A bad FICO score is any score under 580 on the FICO score chart. Your credit score is used to estimate the risk of lending you money. The lower your credit score, the riskier it is to lend you money. People with low credit scores pose more risk compared to others. This is because a bad score is usually associated with poor financial decisions that prevent someone from fulfilling their financial obligations.
Any negative items on your credit report, such as late payments, bankruptcies, accounts in collections, evictions, etc., will lower your credit score. A bad FICO score puts you into the deep prime category of borrowers. The deep prime category means you will be denied loans, credit cards, and business services.
FICO score ranges
Multiple ranges of FICO scores help lenders determine borrowers’ creditworthiness. This means that people within the same range usually qualify for almost the same financial products.
The following are the Ranges of FICO scores.
- Exceptional credit score: 800+. This is the highest range of credit scores. People with exceptional credit scores are considered less risky than any other category of borrowers. An exceptional credit score helps you qualify for the lowest interest rate possible with better terms. Since you will pose less risk, you will qualify for many business services or get discounts.
- Very good credit score: 740-799. A credit score in this range also helps you to qualify for lower interest rates and better terms. Many lenders prefer people in this category or higher because they are less risky.
- Good credit score: 670-739. People in this category qualify for slightly higher interest rates than the first two borrowers categories. The terms and conditions of loans and mortgages for people in this category also get slightly tighter. A good credit score will give you access to many financial products, but your interest rates will be higher than those with very good and exceptional credit scores.
- Fair credit score: 580-669. A fair credit score will qualify you for some financial products, but not all. This range is on the lower side of what lenders accept. For example, you must have at least a 620 credit score for a conventional mortgage.
- Poor credit score: 300-579. This is a range where most lenders don’t even spend a minute evaluating your credit profile or going through your application. People in this range carry the most risk possible in the lending industry. They are more likely to default on their loans than other categories. You might not even qualify for an apartment with a poor credit score.
What is a bad VantageScore?
The VantageScore also ranges from 300 to 850. Any VantageScore under 600 is considered bad. What is a bad or a good VantageScore score? It slightly differs from the FICO score. The VantageScore is calculated by major credit bureaus(Experian, TransUnion, and Equifax).
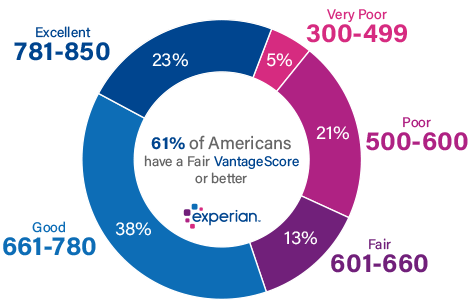
The following are ranges of VantageScores.
- Excellent credit score: 781-850. This is the highest range for VantageScores. People in this range pose less risk than other borrowers, so they qualify for the lowest interest rates and better terms for any financial products they get.
- Good credit score: 661-780. If you cannot reach the top range, this is the next range you should work hard to be in. With a good VantageScore, your terms will still be good, but your interest rates will be slightly higher than the excellent credit score category.
- Fair credit score: 601-660. This is a lower range for many financial products. The terms for this range are stricter, and interest rates are higher. You might not qualify for some loans and services based on your credit history. Your pay rate will be much higher if approved than the top two categories.
- Poor credit score: 500-600. Like the FICO score, people in this range find it extremely difficult to get loans, new credit card accounts, etc. These borrowers are deemed risky and do not qualify for credits.
- Very poor credit score: 300-499. Borrowers in this category of VantageScore have a bad credit history and are the riskiest borrowers on the market. The risk of default is much higher and more frequent for these borrowers. For this reason, lenders do not accept individuals with very poor credit scores.
What affects your FICO score?
The following are factors that affect your FICO score calculation.
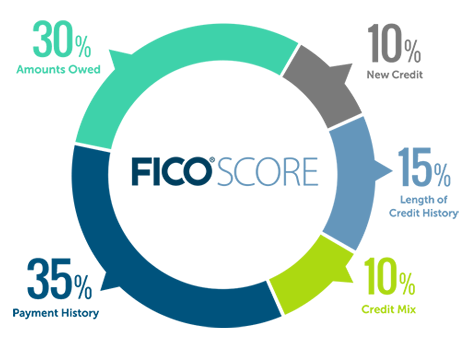
- Payment history: 35%. Your payment history is the most important factor affecting your credit score, accounting for 35% of your FICO score. One late payment can easily lower your credit score by more than 100 points. Pay your bills on time to keep your credit healthy. If you cannot pay your accounts in full, at least pay the minimum requirement on each account. You might still pay the annual percentage rate(APR) on the balance you carried over, but you will not have a late or missed payment on your credit reports.
- Credit utilization: 30%. This is the second factor that affects your credit score. Your credit utilization is the ratio of the amount you spent to the total available credit limit credit. Higher credit utilization shows that you rely on debt to finance your expenses, which makes you a risky borrower. A good rule of thumb is to keep your utilization rate under 30%. The lower your credit utilization rate, the better.
- Age of credit. 15%. This is the average length of how long you have been using credit. The longer you have been responsibly using credit, the better your credit history and credit score will get.
- Credit mix: 10%. This is a combination of different types of credit accounts you have. A good credit mixture is made of revolving credit accounts such as credit cards and nonrevolving accounts such as mortgages and loans.
- New credit: 10%. New credit accounts show on your credit reports as hard inquiries, and each hard inquiry lowers your credit score by 6 points on average.
How do you increase a bad credit score and repair your credit?
A bad credit score is associated with a bad credit history, which reflects bad financial choices. You need a functional strategy to increase your score and repair your credit.
The following are tips to improve bad credit and boost a bad credit score.
- Check your score. Before you improve a bad credit score, you need to know where you stand on the credit score chart.
- Get a copy of your credit reports. Cleaning up your credit reports is a crucial step in improving bad credit. Every activity on your credit accounts is reported to major credit reporting agencies. Any error, inaccuracies, fraudulent activities, or negative information will affect your score. You should always dispute errors and inaccuracies in your credit reports. You can also have all removable negative information deleted from your credit reports.
- Make your payments on time. Your payment history is a major factor in your credit score calculations. If you cannot pay the entire balance monthly, pay the minimum required payment on each credit account.
- Reduce your credit utilization. Your credit score affects how much you spend compared to the total available credit on your accounts. A higher utilization ratio lowers your score. Experts suggest that you stay under a 30% utilization.
- Avoid excessive borrowing. Not only does borrowing too much money increase your risk of financial disaster, but you also lower your credit score every time a new account appears on your credit report.
- Consolidate your debts. If you have financial trouble due to many debts, consider debt consolidation or balance transfer. This could be a debt management strategy that allows you to pay off your debts faster and increase your credit score.
The bottom line
A credit score is one of the most important factors lenders use to estimate how risky it is to lend you money. People with good credit scores get lower interest rates and negotiate better terms. Lenders deny you loans or charge you higher interest rates when you have a bad credit score.
You will have different credit scores since many scoring models exist across different credit reporting agencies. In addition, lenders ask for different credit scores depending on industries.
In general, a bad FICO score is any score under 580, whereas a VantageScore is considered bad when it is under 600.
However, having a bad credit score is not the end of the road. There are strategies you can employ to repair your credit. Some strategies to increase your score and repair your credit are cleaning up your credit reports, making your payments on time, reducing your credit utilization, and avoiding excessive borrowing.