What is gross margin ratio?
The gross margin ratio a.k.a gross profit margin ratio is a financial ratio that measures the profitability of a company in a given period. This ratio helps investors to estimate the percentage of gross sales that stay in the company after covering the cost of goods sold.
A higher ratio indicates that the company is retaining more money from its sales. Retaining more capital helps a business to cover other expenses such as taxes, interest on loans, administrative expenses, etc.
How to calculate the gross margin ratio?
The gross margin ratio is calculated by subtracting the cost of goods sold(COGS) from the net sales, and then, dividing the result by the net sales, according to Accounting Coach.
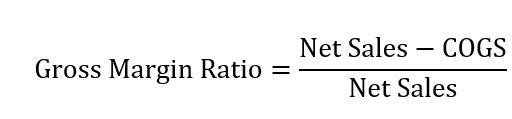
The net sales is the total amount generated from all products and services sold in a given period.
Example
Let’s assume that XYZ company reported net sales of $2,500,000 and the cost of goods sold (COGS) of $1,750,000 on its income statement. What is the gross profit margin?
To answer this question, we will use the following steps.
Step 1: Available data
- Net Sales = $2,500,000
- Cost of goods sold(COGS) = $1,750,000
Step 2: Calculate the ratio
By plugging these numbers in the above formula, we get the following result.
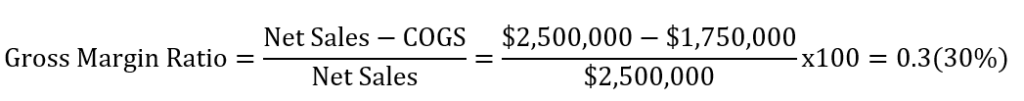
This ratio can be computed in decimal or in percentage. To express the ratio in percentage, you only need to multiply your result by 100.
From our calculations, we can conclude that XYZ company has a gross margin ratio of 0.3 or 30%. This percentage means that for every dollar of sales, only 30 cents will be remaining in the company after covering the cost of goods sold.
How to interpret this ratio?
This ratio tells investors how much a company is retaining from its gross sales. The retained amount (gross margin) helps businesses to cover other expenses related to the business.
Some of these expenses will include but not limited to administrative expenses, operation expenses, taxes, etc.
A company with a higher gross margin ratio covers its remaining expenses easily. In addition, a higher profit margin increases the profitability of a company.
On the contrary, a lower ratio shows that the company is spending most of its money on the cost of goods and services it sells. As noted by Investopedia, the gross margin helps investors and companies to understand the relationship between production costs and revenues.
Retaining less money from sales makes it difficult for a company to cover other expenses. This can hinder the company’s future growth and profitability.
More learning resources
- Payables Turnover Ratio Definition
- Receivables Turnover Ratio Definition
- Price To Earnings (P/E) Ratio: What Is P/E Ratio?
- Price-To-Book (P/B) Ratio: What Is P/B Ratio?
- Dividend Payout Ratio And How It Works
- What Is Asset Turnover Ratio? How Does It Work?
- Price-To-Sales (P/S) Ratio: What Is P/S Ratio?
- What Is Inventory Turnover Ratio?
- Quick Ratio: What Is Quick Ratio?
- Current Ratio: What Is The Current Ratio?