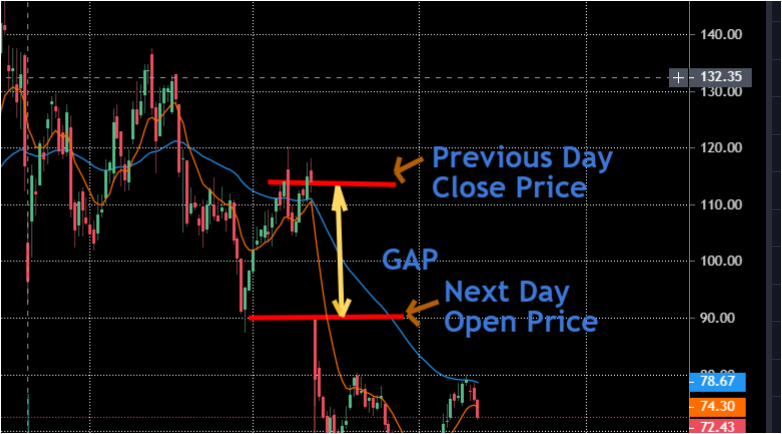
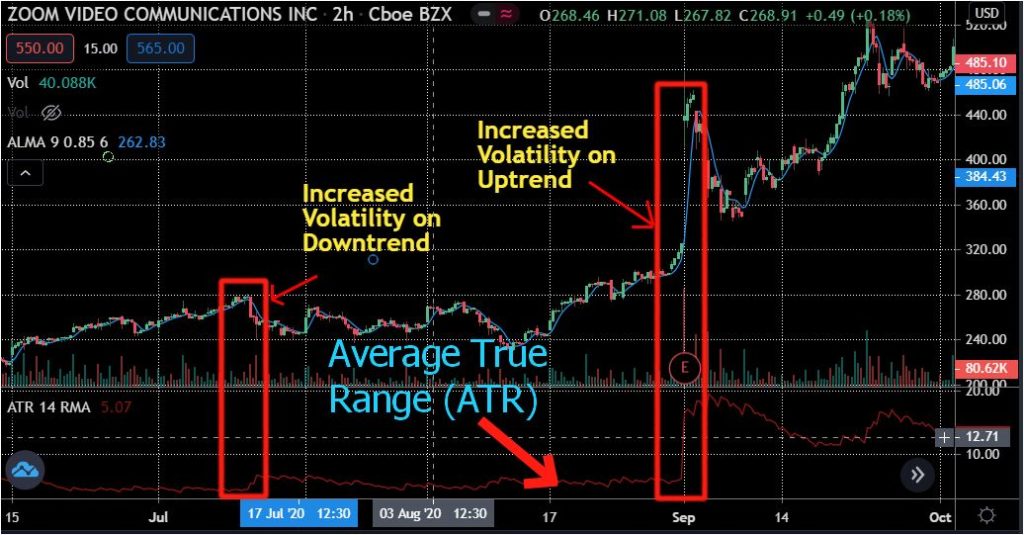
What is debt ratio?
A debt ratio is a financial ratio that measures the percentage of a company’s total assets that are being financed by debt. This ratio helps investors to understand the amount of leverage a company has taken. More leverage comes with high risks and less independence.
On the other hand, a lower ratio indicates that the company does not depend on debt to finance its assets. In other words, the company is more stable and less risky for investors.
Formula of debt ratio
The debt ratio compares total assets and total debt a company has, and therefore, use these two parameters when calculating the ratio. That is the debt ratio is the ratio of total debt to the total assets [credit: Ready Ratios].
To express the ratio as a percentage, you will multiply the result by 100.
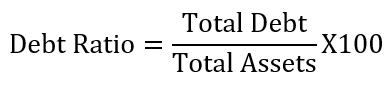
Example
Let’s assume that XYZ company has $250,000 in assets and $175,000 in total liabilities. What is the debt ratio?
To answer this question, we will use the following steps.
Step 1: Available data
- Total Assets = $250,000
- Total Liabilities = $175,000
Step 2: Calculate the ratio
By plugging these two numbers into the above formula, we will have the following ratio.
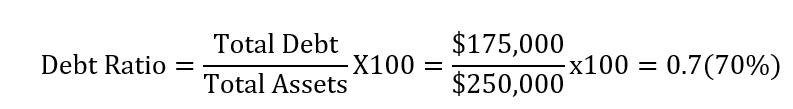
From our calculations, we can conclude that XYZ company has a debt ratio of 0.7 or 70%. In other words, 70% of its total assets are financed through leverage.
Why does the debt ratio matters?
The debt ratio measures how a company’s assets are financed. A higher ratio indicates that the company has accumulated more debt. Whereas a lower ratio indicates that the company does not rely on debt to finance its operations.
This ratio comes in handy when investors are evaluating companies. Usually, businesses with more debt are prone to financial difficulties. For this reason, it is difficult to achieve steady growth and profitabilities.